Mobile Cloud Computing
Mobile Cloud Computing
What is Mobile Cloud Computing?
Mobile devices are restricted by the hardware that is encased within the device. They are constrained to their processing power, storage, and battery life. Meanwhile, cloud computing allows the user to have infinite computing resources since they can tap into data centers that are located in other places. Mobile cloud computing is the combination of mobile devices with cloud computing capabilities. The cloud will perform all of the computing-intensive tasks, so the mobile device is no longer restricted by the hardware within the device. In the mobile cloud computing platform, data processing and data storage happen outside of the mobile device. (Hossain, 2016)
Architecture of Mobile Cloud Computing
Figure 1 shows the diagram for the architecture of mobile cloud computing.
Figure 1. Mobile cloud computing architecture
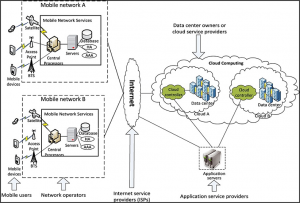
Source: Ahire, 2017
As shown in figure 1, mobile devices are connected to mobile networks by base stations (Satellite, Access point, or Base transceiver station). Base stations establish and control the connections and functional interfaces between the mobile devices and the networks. Requests and information from mobile users are transmitted to the central processors. Central processors are connected to servers which provide mobile network services. The users request then gets delivered to the cloud through the internet. Once the request is in the cloud, cloud controllers process the requests to ensure that the user is provided with the correct corresponding cloud services. (Ahire, 2017)
Advantages of Mobile Cloud Computing
Using a mobile cloud computing platform generates several advantages for mobile devices and helps overcome numerous issues.
- Extended battery life – Using the cloud to complete tasks allows your mobile device to consume less energy which will help save on battery life.
- Ease of integration – Services from different service providers can be integrated easily on a mobile device
- Improved reliability – The cloud can back up your data on numerous cloud servers which can reduce data lose on a mobile device. The cloud can also provide security services like virus scanning.
- Scalability – Easy to add and expand services without worrying about hardware capabilities.
- Improved processing power – The cloud will help reduce energy and increase efficiency when running intensive programs.
- Improved data storage capacity – The user will no longer have a constraint on storage for mobile devices. They will have access to unlimited storage provided by the cloud.
- Improved synchronization of data – The cloud will upload the user’s data to a centralized database and then push the information to all of their other devices. This allows the information to be consistent and accurate over all the users devices.
All of these advantages can only be achieved once the mobile device no longer is constrained to the hardware within. Since everything can be accessed from the cloud, the mobile device only has to act as a screen. (Hossain, 2016)
Concerns of Mobile Cloud Computing
People have always had concerns and fears when it comes to cloud computing. Some of these concerns include privacy, data ownership, and security. These concerns are also very relevant to the area of mobile cloud computing.
Privacy. There is one type of application that normally raises privacy concerns for mobile cloud computing. This application is location-aware applications and services. These applications and services perform tasks that require knowledge of the user’s location. For example, google maps asking the user to enable their location so it can show the users location without the user typing it in. One way to try and fix this concern is through location cloaking. Location cloaking is when the user’s exact location is blurred, and they are placed into cloaked regions. Although this helps calm concerns, it reduces the quality of service that an app can offer the user. (Shanklin, n.d)
Data Ownership. There are major concerns with data ownership specifically concerning the ownership of purchased digital media. The cloud allows purchased media files (Audio, video, or e-books) to be stored remotely rather than locally. This raises the concern of true ownership of the data. For example, if a user purchases media using a given service and the media itself is stored in the cloud, the user could lose access to the purchased media. This happened to amazon customers in July of 2009. All owners of the e-book 1984 by George Orwell were refunded and Amazon removed the book from all devices. Amazon discovered the publisher of that specific e-book did not have the right to sell or distribute it. This actioned cause people to be outraged because they believed the book was their property. (Shanklin, n.d.)
Data Access and Security. Many people have concerns and fears with data access and security. The user can be significantly affected if an application relies on remote data storage and internet access in order to function. For example, if a user stores all of their contacts on the Apple cloud and Apple experiences outages, then the user cannot access the information until the outage is fixed. Depending on the information stored in the cloud, it can affect the user’s ability to function from day to day. Mobile cloud computing is vulnerable due to the multiple points of access that can be interrupted. There can also be issues with data becoming locked in a particular service. (Shanklin, n.d.)
Apple iCloud on iPhones
iCloud is a cloud storage and computing service provided by apple. This helps store all the user’s photos, videos, documents, music, apps, etc. Once the information is stored, it is pushed to all of the user’s apple devices. Figure 2 shows a diagram of how the process works. (What is iCloud?, n.d.)
Figure 2. Diagram for the process of iCloud
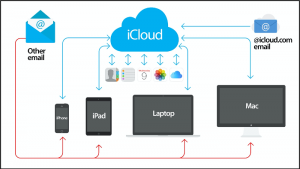
iCloud allows the user to upgrade data storage. This means that your iPhone can have customizable storage through iCloud. If the user starts to run low on storage, they can upgrade the storage on iCloud and transfer their files, so they are stored in the cloud. This demonstrates improved data storage capacity through mobile cloud computing.
How Mobile Cloud Security Relates to the Material Covered in MIS3406
In MIS3406 we learned to create a cloud-based application that is hosted on AWS. Mobile devices have become essential in our society and applications have to be designed to take advantage of them. Mobile cloud computing will help distribute applications easily to mobile devices and improve the efficiency of running the application on mobile devices. The learning objectives for MIS3406 are:
- Understand the concepts of modern cloud computing
- Build a cloud application deployment infrastructure using AWS
- analyze and configure a cloud infrastructure for scaling and redundancy
- Develop a simple RESTful API using Node.js
- Deploy an API to a cloud infrastructure using instance-based and application-based methods
In order to build applications, the developer has to take into account all of the devices that will run the application. Mobile cloud computing will allow all applications to run on mobile devices even if the application is very complex.
How Mobile Cloud Computing Relates to Cloud Security
Cloud Security is important in all aspects of the cloud especially in mobile cloud computing. Mobile cloud computing can have important data stored like credit card information, current location, contacts, important notes, pictures, etc. This information must be secured and protected from outsides attacks. Cloud security will help secure mobile cloud computing applications by eliminating any weak points into the network. When applications are built on a mobile cloud computing platform, security must be built-in in order to protect all of the data that is running through or stored on the application.
References:
Ahire, J. B. (2017, December 29). MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING: PART 1. Retrieved April 27, 2020, from https://medium.com/@jayeshbahire/mobile-cloud-computing-part-1-16c5ed408507
Hossain, S. (2016, September 15). What is mobile cloud computing? Retrieved April 27, 2020, from https://www.ibm.com/blogs/cloud-computing/2014/01/02/what-is-mobile-cloud-computing/
Shanklin, M. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2020, from https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-10/ftp/cloud/index.html
What is iCloud? (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2020, from https://support.apple.com/guide/mac-help/what-is-icloud-mh36832/mac

